Topgene Research Institute
Hubei Topgene Biotechnology Research Institute Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Topgene Research Institute) is the core research and development institution of Hubei Topgene Biotechnology Co., Ltd. It is located at No. 12 Sandao Street, Wuchang District, Wuhan City (formerly within Hubei Pharmaceutical Industry Research Institute). With the core mission of "Service for Medical Innovation & Dedication to Life and Health", Topgene Research Institute focuses on the development of non-human primate (NHP) and rodent models for human diseases, providing services for the pharmacodynamics (PD), pharmacokinetics (PK), and pre-toxicity evaluation of various drugs (biotechnological drugs, chemical drugs, traditional Chinese medicine). It offers professional and efficient non-clinical drug research services for pharmaceutical companies, research institutes, and universities engaged in drug development. The institute covers approximately 2,800㎡, including 1,000㎡of laboratories and 1,500㎡ of animal facilities (280㎡for barrier environments and 1,220㎡for conventional environments). The institute is capable of conducting experiments on conventional monkeys, dogs, small pigs, rabbits, as well as SPF-grade rats, mice, and guinea pigs. Topgene Research Institute currently has platforms for non-human primate surgery, behavioral studies and analysis, experimental animal molecular imaging, in vivo electrophysiology (under construction), cell molecular biology, biological analysis, and pathological analysis.

Service Platform
Monkey Surgery-related Platform
1.Anaesthesia
2.Multiple brain surgeries and brain stereotaxic infusion
3.Lateral ventricle capsule implantation
4.Splenectomy
5.Ultrasonic-guided surgical technique
6.Customized surgical services
7.Intensive care
Monkey Behavioral Platform
1.Cognitive ability measurement: WGTA (Wisconsin general test apparatus), Cantab (Cambridge neuropsychological test automated battery).
2.Motor-related skill detection: Kurlan score, primate scan, fine finger coordination assay, food-grasping task.
3.Emotion-related behavioral analysis: Spontaneous activity analyses, huddle, day-time sleeping, human intruder test, pace, turn in circles, face the wall, etc.
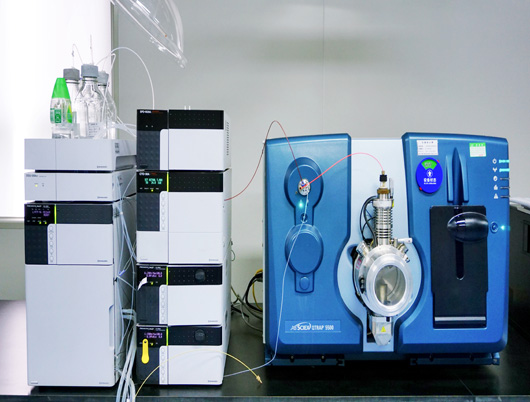
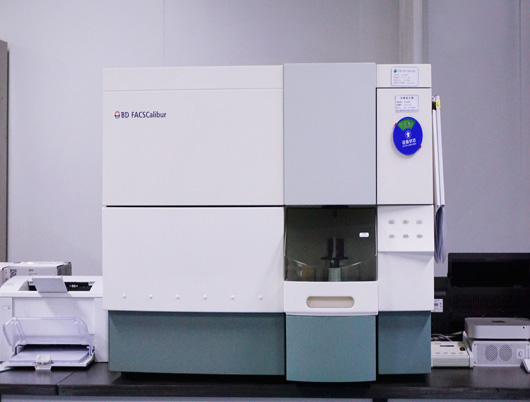
Bioanalysis Platform
1.Antibody drug analyses
2.Nucleic acid drug analyses
3.Peptide drug analyses
4.Biomarker analyses
5.Anti-drug antibody analyses
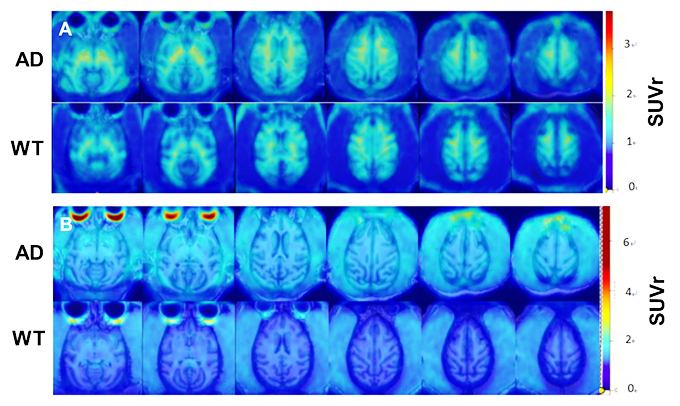
Molecular Imaging Platform
1.Radionuclide labeling and probe synthesis: 124I、89Zr、64Cu、68Ga、18F、AV45(Aβ)、T807(Tau).
2.Image acquisition, fusion and data analysis: PET/CT, MRI/fMRI, PET/MRI.
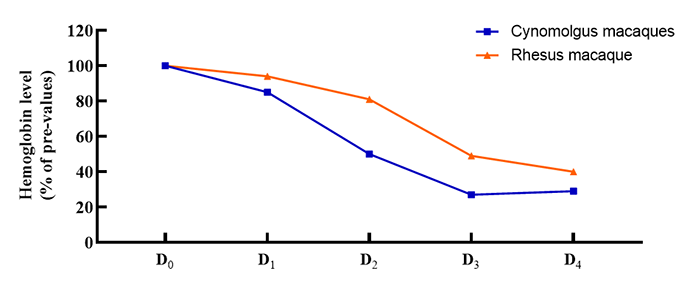
3.Scope of application: PK/PD, ADME, dose range test and safety evaluation; disease model evaluation, pathogenesis study, drug targeting evaluation, etc.






 Branch Institutions
Branch Institutions